Dental problems are among the most common health issues worldwide, yet many people ignore early signs until pain or damage becomes severe. Learning about these dental issues and how to prevent them can help you protect your teeth and gums for a lifetime, lowering your treatment costs. In this guide, we’ll cover the most common dental problems, explain their causes, and share practical ways to prevent them. By the end, you’ll recognize most of your symptoms, know how to prevent dental problems, and decide when to get help from a dentist.
What Are Common Dental Issues?
From minor issues like bad breath to serious conditions that require extensive treatments, dental problems can range in severity and complexity. Early identification and proper management are crucial for preventing complications and maintaining long-term oral health. Let’s learn about these problems.
1. Tooth Decay (Cavities)
Tooth decay is one of the most common oral health issues, affecting both children and adults. It occurs when bacteria in the mouth feed on sugars from food and drinks, producing acid that slowly erodes the enamel. Over time, this damage creates small holes or cavities.
Cavities may not cause pain at first, but as they deepen, they can lead to tooth sensitivity, toothache, and even infection if bacteria reach the inner pulp. If untreated, decay can spread to neighboring teeth or require more complex procedures like root canal therapy or extractions.
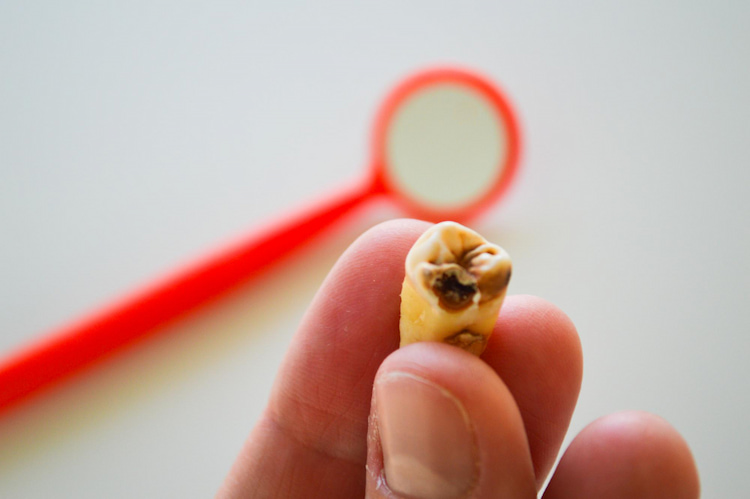

Want to learn more about tooth decay? This article is for you: What is Tooth Decay: Causes, Prevention, and Treatment
2. Gum Disease (Gingivitis & Periodontitis)
Gum disease starts with gingivitis, which causes red, swollen, and bleeding gums. At this stage, it’s often painless and easily overlooked. If left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, a more serious condition where infection spreads to the supporting bone and tissues around the teeth.
Periodontitis can cause gum recession, loose teeth, and eventually tooth loss. Research also links advanced gum disease to systemic health conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and stroke, making it a condition that affects more than just the mouth. Periodontics services can diagnose and manage types of gum disease and help restore your oral health.
3. Tooth Sensitivity
Tooth sensitivity is the sharp pain or discomfort experienced when consuming hot, cold, sweet, or acidic foods and drinks. It usually occurs when the enamel thins out or gums recede, exposing the sensitive dentin underneath. Other causes include cracked teeth, worn fillings, or teeth grinding. While sensitivity is common, persistent discomfort may indicate a deeper dental problem, such as decay or gum disease, that requires treatment.
If you’re dealing with sensitive teeth, make sure to use the right toothpaste. This guide helps you choose the correct item: Best Toothpaste for Sensitive Teeth After Whitening
4. Bad Breath (Halitosis)
Occasional bad breath is normal, especially after certain foods. However, chronic halitosis often signals an underlying issue. Poor oral hygiene is the most common cause, as bacteria in the mouth release foul-smelling compounds. Since bad breath can affect social confidence and quality of life, identifying the root cause is important for effective treatment.
Did you know there are mouthwashes suitable for bad breath? Read more here: What Is the Best Mouthwash for Bad Breath?
5. Tooth Erosion (Enamel Wear)
Tooth erosion occurs when acids, either from diet (soda, citrus, wine) or medical conditions like acid reflux, dissolve tooth enamel. Unlike cavities, which result from bacterial action, erosion is caused by direct acid attack on enamel. Over time, erosion can make teeth appear thinner, smoother, or discolored. It also increases the risk of sensitivity and cavities because enamel does not grow back once lost.
6. Cracked or Chipped Teeth
Cracks or chips can result from accidents, biting hard foods, or grinding teeth at night. Sometimes the damage is purely cosmetic, but deeper cracks can expose the tooth pulp and lead to severe pain or infection. Symptoms vary; some cracks are visible, while others are microscopic and only detected with dental imaging. Left untreated, cracked teeth may worsen and eventually require tooth extraction.
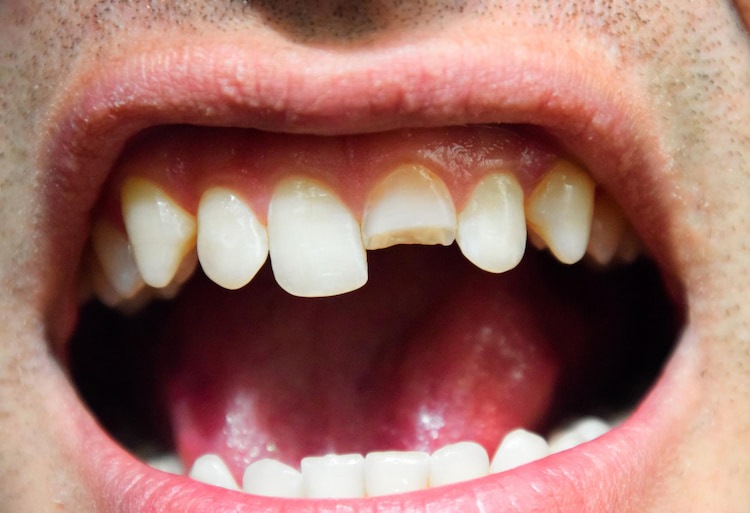
7. Toothache
Dental pain is a warning sign, not a condition itself. It can result from cavities, abscesses, gum disease, cracked teeth, sinus infections, or even nerve-related issues. The pain may be sharp, throbbing, or constant, sometimes spreading to the jaw or ear. Because toothaches often indicate infection or decay, they should never be ignored. Delaying treatment may worsen the problem and make saving the tooth more difficult.
8. Oral Cancer
It includes cancers of the lips, tongue, cheeks, and throat. It often starts as persistent sores, lumps, or white or red patches in the mouth. In many cases, patients don’t notice early symptoms until the cancer has advanced. Risk factors are tobacco use, heavy alcohol consumption, HPV infection, and prolonged sun exposure on the lips. This life-threatening dental issue has a much higher survival rate when detected early through an oral cancer exam.
9. Dry Mouth (Xerostomia)
When the salivary glands don’t produce enough saliva, you get dry mouth. Saliva is crucial for washing away food particles, neutralizing acids, and protecting against cavities. Dehydration, certain medications, aging, or conditions like diabetes can lead to this issue. Chronic dry mouth not only feels uncomfortable but also increases the risk of cavities, gum disease, and bad breath.
According to NIDCR, you can relieve dry mouth by drinking plenty of water throughout the day, sipping water or sugarless drinks with meals, and chewing sugarless gum or sucking on sugar-free candies to stimulate saliva. Limiting caffeine, avoiding alcohol and tobacco, and using a humidifier at night are helpful too.
10. Impacted Teeth (Especially Wisdom Teeth)
These are teeth that fail to emerge fully into the mouth, often due to a lack of space. Wisdom teeth are the most commonly impacted. They can remain trapped in the jawbone or gum tissue, causing pain, swelling, infection, or damage to neighboring teeth.
In some cases, impacted teeth may not cause symptoms but still pose risks, such as shifting other teeth or forming cysts. Dentists usually monitor impacted teeth with X-rays to decide if extraction is necessary.
11. Bruxism (Teeth Grinding & Clenching)
Dental bruxism often happens unconsciously, especially during sleep. Over time, grinding and clenching can wear down enamel, cause jaw pain, headaches, and even damage fillings or crowns. Many patients are unaware of their bruxism until their dentist notices signs of tooth wear. Stress, anxiety, and sleep disorders are common contributing factors.
12. Tooth Discoloration (Stains & Yellowing)
Whether external (surface stains from coffee, tea, smoking, or wine) or internal (caused by trauma, aging, or certain medications), tooth discoloration may sometimes signal underlying enamel or dentin damage. Stained teeth can affect self-esteem, but treatments such as professional dental cleaning or teeth whitening can restore brightness.
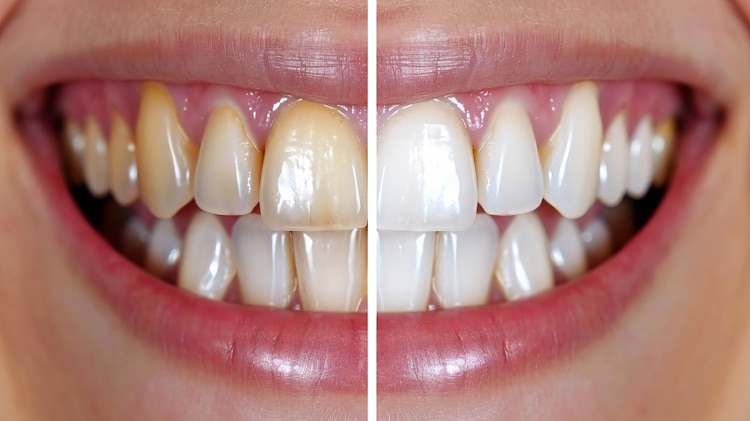
Learn more about the cost of dental cleaning here: How Much Does a Teeth Cleaning Cost?
13. Dental Abscess
A dental abscess is a pocket of pus caused by bacterial infection, usually from untreated cavities, gum disease, or injury. Symptoms are an intense toothache, swelling, fever, and sometimes a foul taste in the mouth. Please remember that abscesses require urgent treatment. If left untreated, the infection can spread to other parts of the body, leading to serious health complications.
14. Receding Gums
Gum recession exposes the roots of teeth, making them look longer and causing sensitivity. It often develops gradually, caused by gum disease, aggressive brushing, bruxism, or genetics. Exposed roots are more prone to decay, and severe gum recession can eventually lead to tooth loss if untreated.
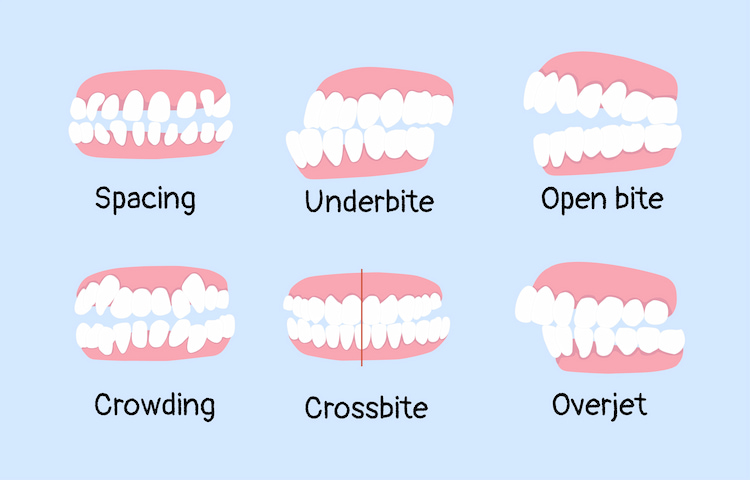
15. Tooth Misalignment / Malocclusion
Misaligned teeth include crowding, overbite, underbite, and spacing issues. Beyond affecting appearance, malocclusion can make chewing difficult, cause uneven tooth wear, and increase the risk of cavities in hard-to-clean areas. Overbite, underbite, crossbite, and open bite are all different types of malocclusion. Orthodontic treatments not only improve aesthetics but also prevent long-term functional problems.
16. Jaw Pain (TMJ Disorder)
TMJ (temporomandibular joint) disorders affect the hinge connecting your jaw to your skull. Someone with this disorder experiences jaw pain, difficulty chewing, clicking or popping sounds, and even headaches. TMJ disorders can be caused by arthritis, injury, stress, or teeth grinding. They often require a combination of dental care, lifestyle changes, and sometimes physical therapy.
17. Plaque and Tartar Buildup
Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that forms constantly on teeth. If not removed with brushing and flossing, it hardens into tartar, which can only be removed by a dentist. Tartar buildup increases the risk of cavities, gum disease, and bad breath, and it often appears as yellow or brown deposits around the gumline.
18. Tooth Loss
Tooth loss can occur due to trauma, gum disease, or severe decay. Missing teeth not only affect appearance but also chewing ability, speech, and jawbone health. Over time, untreated tooth loss can cause neighboring teeth to shift, leading to bite problems and further dental issues. Modern treatments such as implants, bridges, and dentures offer effective solutions.
19. Root Infection
A root infection occurs when bacteria invade the pulp of the tooth through deep decay, cracks, or trauma. It often causes severe pain, swelling, and sometimes abscess formation. If untreated, root infections can spread to surrounding tissues or even enter the bloodstream. Root canal therapy is usually required to save the tooth.
Contact Us for Help!
Protect your smile before problems arise. Schedule a preventive dental check-up at Pape Dental Centre today and let our team help you maintain strong, healthy teeth.
How to Prevent Dental Problems?
Prevention is the foundation of dental health. Below, we have listed the most effective oral health care tips.
- Use soft-bristled toothbrushes and gentle brushing techniques to avoid enamel wear.
- Limit acidic foods and beverages that can erode protective enamel.
- Wait at least one hour after eating acidic foods before brushing teeth.
- Use fluoride treatments to strengthen enamel and reduce sensitivity.
- Avoid whitening products that may temporarily increase tooth sensitivity.
- Use antimicrobial mouthwash to reduce bacterial populations in the mouth.
- Quit smoking and tobacco use, which significantly increases gum disease risk.
- Manage diabetes and other systemic conditions that affect gum health.
- Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins C and D to support immune function.
- Stay hydrated to maintain adequate saliva production for natural cleaning.
- Replace ill-fitting dental appliances that may irritate gums.
Final Word
Dental problems are common, but most are preventable with the right care. From cavities and gum disease to more serious issues like oral cancer, being proactive with your oral health can save you from pain, costly treatments, and long-term damage.
At Pape Dental Centre, our mission is to help you maintain a healthy, confident smile for life. We offer various general dental services to protect your dental health and provide you with cosmetic dental treatments on Danforth to keep your smile bright and shiny!
Book your appointment with Pape Dental Centre today and take the first step toward stronger teeth and gums.
FAQ
-
How to fix rotten teeth without a dentist?
Unfortunately, rotten teeth cannot be fixed at home. While good oral hygiene can slow further damage, professional treatment like fillings, crowns, or extractions is required.
-
At what age do adults start losing teeth?
Healthy adults should not lose teeth naturally. Tooth loss is usually due to gum disease, decay, or injury, not age. With proper care, you can keep your teeth for life.
-
How long do teeth last without brushing?
Plaque begins to form on your teeth just a few hours after you stop brushing. If you go one to two days without brushing, your breath will worsen, plaque will harden into tartar, and your gums may start to get irritated. After a week or more, your risk of cavities, gum disease, and bad breath increases significantly. Over months or years without brushing, teeth can decay, gums can recede, and tooth loss becomes likely.
-
How many 70-year-olds still have all their teeth?
Thanks to modern dentistry, many older adults keep most or all of their natural teeth. Studies show that about 50-60% of people in their 70s still have most of their teeth if they maintain good oral care.
-
Is age 5 too early to lose teeth?
No. Most children start losing baby teeth around age 5-7. However, if teeth fall out much earlier, consult a dentist to ensure proper development.
We’d love to hear from you! Have you experienced any of these dental problems? Share your story in the comments below; we might feature your question in our next blog.

