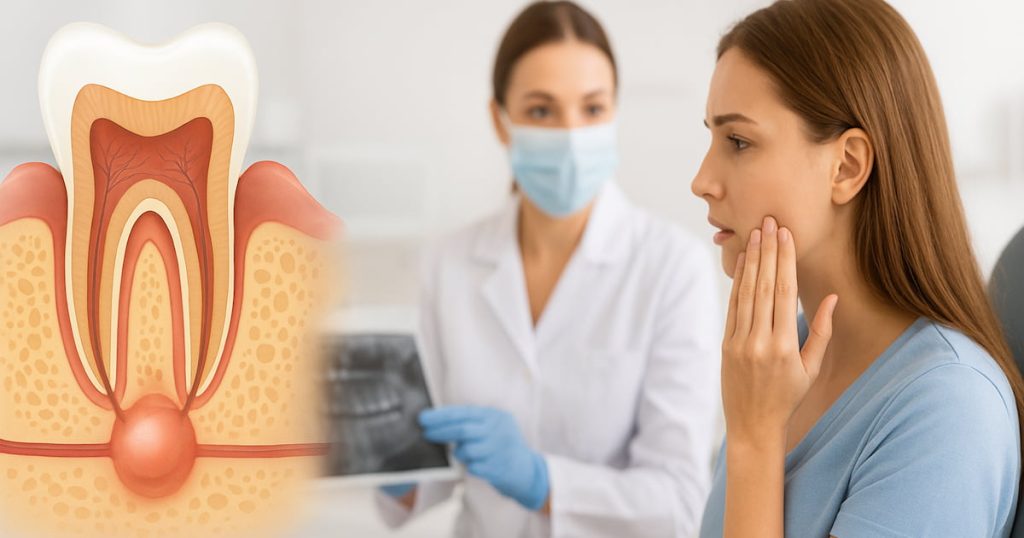
Dental health isn’t just about your teeth; there is one condition that typically requires oral surgery and can affect tissues and bones, which is called a dental cyst. Taking dental cyst treatment seriously is crucial. Why? Although these fluid-filled sacs are unnoticed at first, they grow and can lead to infections, bone damage, or tooth loss.
In this article, we’re going to explain dental cysts’ causes, symptoms, and discuss effective treatment options to help you stay more informed and confident about your oral health.

What is a Dental Cyst?
Before discussing dental cyst treatment, we should first understand what a dental cyst is. A dental cyst is a sac filled with fluid that forms in the jawbone or soft tissues of the mouth. It often appears near the roots of teeth, which makes it, as you can guess, painful. These cysts are usually lined with epithelium and can vary in size. While many cysts are benign and cause no harm, they can lead to complications if left untreated.
Dental cysts have different types and are generally categorized into odontogenic and non-odontogenic cysts. The most common types of odontogenic cysts include:
Periapical (radicular) Cyst
It’s the most common type of dental cyst and usually develops when the inside of a tooth dies, often because of untreated cavities or injury. The cyst forms at the tip of the non-vital tooth and is linked to a long-term infection in the surrounding bone.
Dentigerous Cyst
This cyst forms around the crown of an unerupted or developing tooth, like impacted third molars (wisdom teeth) and maxillary canines.
Odontogenic Keratocyst (OKC)
This cyst is known for growing quickly and coming back even after treatment. In some cases, it is linked to a rare genetic condition called Gorlin-Goltz syndrome, which can cause multiple cysts and other health issues.
Gingival Cyst
This rare cyst occurs in the soft tissues of the gums and is often like a small, painless swelling. Gingival cysts can be found in both newborns and adults.
Causes of Dental Cysts
| Causes | How does it form the cyst |
| Infection and inflammation | When the tooth pulp becomes necrotic due to untreated cavities. |
| Development issues | When fluid accumulates between the crown of an unerupted tooth and the surrounding dental follicle. |
| Trauma | Physical injury may cause a tooth to die without immediate symptoms, and the development of a cyst at the site. |
| Impacted teeth | The pressure and inflammation from impaction can cause cyst formation. |
| Genetic factors | Some genetic conditions, like Gorlin-Goltz syndrome, can be associated with the formation of multiple cysts. |
| Poor oral hygiene | Poor oral hygiene can lead to gum disease and tooth decay, which increases the risk of infections and, as a result, cyst formation. |
Read More: Oral Health Care Tips: Essential Tips for Healthy Teeth and Gums
Symptoms of a Dental Cyst
It’s important to always visit your dentist for check-ups at regular intervals, so if needed, you can get dental cyst treatment at an early stage. As mentioned earlier, many dental cysts are asymptomatic in their early stages, but they can lead to noticeable symptoms when they grow or become infected. Here are the symptoms to watch for, so you can see your dentist immediately if they appear:
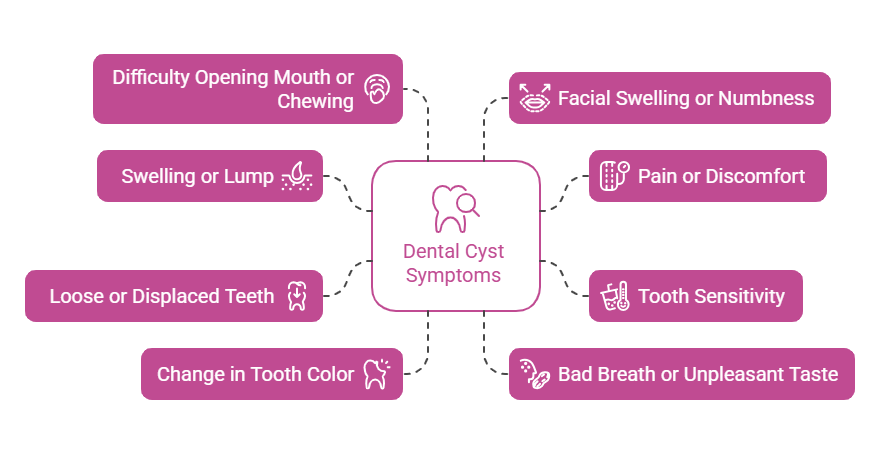
- Swelling or a lump in the gums or jaw: The swelling or lump, which is initially painless, can develop in the affected area. Note that this cyst can become painful if infected.
- Pain or discomfort: The cyst can add pressure on surrounding tissues while growing, and this leads to pain in the affected tooth or jaw area.
- Tooth sensitivity: When cysts pressure on the tooth’s nerve endings, it may become sensitive to hot and cold temperatures or to sweet foods and drinks.
- Loose or displaced teeth: A growing cyst can cause adjacent teeth to become loose or shift from their place. This leads to gaps or misalignment.
- Change in tooth color: Nerve damage or infection associated with a cyst can show itself in a darker, gray, or yellowish color.
- Bad breath or unpleasant taste: An infected cyst can produce pus that leads to bad breath or foul taste in the mouth.
- Difficulty opening the mouth or chewing: Large cysts may lead to difficulty opening the mouth fully or pain while chewing.
- Facial swelling or numbness: The cyst that presses on facial nerves can cause swelling or numbness in the face, lips, or chin.
Read More: How to Avoid Bad Breath?
Prevent The Damages Caused By Dental Cysts
If you’re experiencing symptoms or want a check-up to ensure your mouth is cyst-free, we’re here to help you. At Pape Dental Clinic, we take care of your oral health with an expert and compassionate team.
How is a Dental Cyst Treated?
Dental cyst treatment depends on factors such as the size, location, type, and whether it’s infected. For preventing complications like infection, bone loss, or tooth displacement, early diagnosis is crucial. Here are some of the treatments for dental cysts:
Surgical Removal
This is the most common and effective dental cyst treatment, which involves removing the entire cyst along with its epithelial lining to reduce the risk of recurrence. It depends on the size and location of the cyst, though in some cases, removing the adjacent teeth or bone may be needed.
Root Canal Treatment
This treatment might be necessary if the cyst is associated with a necrotic or infected tooth pulp. In this procedure, the infected pulp tissue is removed, then the root canal system is disinfected and sealed to prevent further infection. Root canal treatment is helpful to preserve the affected tooth.
Antibiotic Therapy
For infected cysts, antibiotics may be prescribed to control the infection before or after surgical treatment. According to PubMed, antibiotics reduce the bacteria present in the cyst fluid. However, antibiotics alone are not sufficient to treat dental cysts, but they are used with other treatments.
Conclusion
Dental cyst treatment should never be ignored because if left untreated, it can grow and cause discomfort or serious complications. An infected cyst can lead to serious oral complications. If you notice pain, swelling, or unusual changes in your teeth, it’s important to consult a dentist for dental cyst treatment.
Here at Pape Dental Centre, we offer a wide range of dental services for families and consult with patients for their needs.
FAQs
-
How serious is a dental cyst?
Dental cysts are normally benign, but if they remain untreated, they can cause infections, damage surrounding teeth or bone, and finally, tooth loss.
-
How to get rid of a dental cyst?
It depends on the cyst’s size and place, but typically they’re removed either completely or through drainage and decompression.
-
How painful is dental cyst removal?
This type of procedure is done under local or general anesthesia, and as a result patient won’t feel pain during surgery. However, mild discomfort is expected, which is manageable with pain relievers.
-
How long does it take to recover from dental cyst surgery?
Recovery takes one to two weeks unless the surgery is extensive, which requires a longer healing period. Although after a few days, patients can continue normal activities.
-
Can a dental cyst be removed without surgery?
There are non-surgical options, but they are limited and aren’t as effective as surgery. In most cases, surgical removal is necessary.
If this article helped you recognize symptoms of a dental cyst, feel free to share your experience in the comments.